A business is an organization or entity engaged in commercial activities to earn profit by providing goods or services to customers. Whether it’s Apple selling innovative technology or a local bakery serving fresh bread, businesses form the backbone of our economy and drive innovation, employment, and economic growth worldwide.
Understanding what constitutes a business goes beyond simple profit-making. Modern businesses operate as complex entities with various structures, sizes, and purposes. From entrepreneurship ventures to multinational corporations, each business type serves unique market needs while contributing to economic development. The digital transformation strategies adopted by contemporary businesses have further evolved how we define and operate commercial enterprises.
This comprehensive guide explores the fundamental concepts of business, from basic definitions to complex organizational structures. You’ll discover the different types of businesses, understand company size classifications, and learn essential business terminology that every aspiring entrepreneur or business professional should know.
Table of Contents
What Defines a Business?
A business represents any organization that seeks to profit by providing goods or services that satisfy customer needs. The fundamental purpose involves creating value through the transformation of inputs (resources, labor, materials) into outputs (products or services) that customers are willing to purchase.
Key characteristics of businesses include:
- Profit motive: Primary goal of generating financial returns
- Customer focus: Meeting market demands and consumer needs
- Value creation: Transforming resources into valuable offerings
- Risk assumption: Accepting uncertainty in pursuit of rewards
- Organized structure: Systematic approach to operations and management
Businesses operate within legal frameworks that define their rights, responsibilities, and operational parameters. They must comply with regulations, pay taxes, and maintain proper documentation of their activities. The business registration number serves as a unique identifier that legitimizes operations and enables government tracking.
For those interested in exploring business fundamentals further, comprehensive business guides provide detailed insights into various operational aspects and strategic considerations.
Different Types of Business Structures
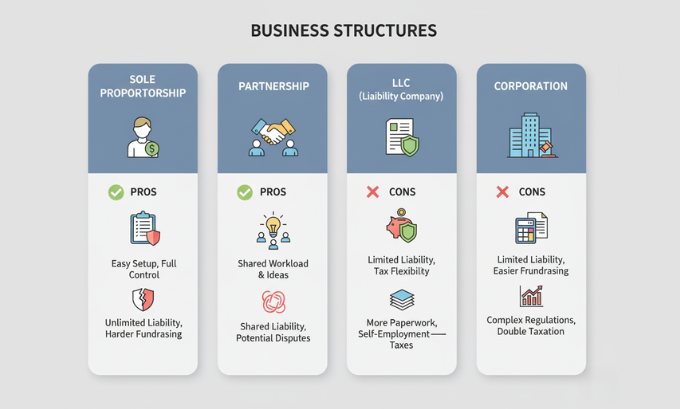
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship represents the simplest business structure where one individual owns and operates the entire enterprise. This structure offers complete control but also places unlimited liability on the owner.
Advantages:
- Easy setup with minimal paperwork
- Complete decision-making authority
- Direct access to all profits
- Simple tax reporting
Disadvantages:
- Unlimited personal liability
- Limited access to capital
- Business ends with owner’s death or incapacity
- Difficulty attracting investors
Partnership
Partnerships involve two or more individuals sharing ownership, responsibilities, and profits. What is a business partnership fundamentally comes down to shared risk and reward among multiple parties.
Types of partnerships:
- General Partnership: All partners share equal responsibility and liability
- Limited Partnership: Combines general partners (unlimited liability) with limited partners (liability restricted to investment)
- Limited Liability Partnership (LLP): Provides liability protection while maintaining partnership tax benefits
Corporation
Corporations exist as separate legal entities distinct from their owners (shareholders). This structure provides the strongest liability protection but involves more complex regulations and tax requirements.
Corporate characteristics:
- Limited liability protection for shareholders
- Ability to issue stock and raise capital
- Perpetual existence beyond founders
- Complex regulatory requirements
- Double taxation (corporate and personal levels)
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
LLCs combine corporation liability protection with partnership tax flexibility. This hybrid structure has become increasingly popular among small and medium-sized businesses.
LLC benefits:
- Limited liability protection
- Flexible management structure
- Pass-through taxation options
- Fewer regulatory requirements than corporations
Understanding how to scale a business successfully often depends on choosing the appropriate business structure that supports growth objectives and operational requirements.
Understanding Company Sizes
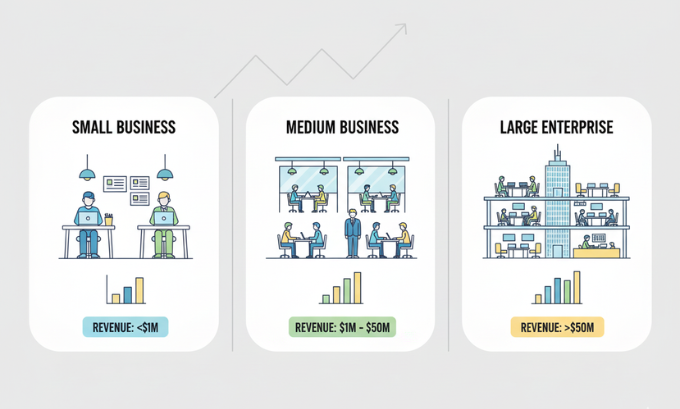
Small Businesses
Small businesses typically employ fewer than 500 employees and generate limited annual revenue compared to larger enterprises. The Small Business Administration (SBA) provides specific size standards that vary by industry.
Small business characteristics:
- Limited number of employees (usually under 100)
- Annual revenue under industry-specific thresholds
- Local or regional market focus
- Owner-operated or closely held management
- Limited access to capital markets
Small businesses represent the backbone of most economies, providing employment opportunities and serving local communities. They often benefit from SBA programs offering business lines of credit, grants, and mentorship support.
Medium-Sized Businesses
Medium-sized businesses occupy the space between small enterprises and large corporations. They typically employ between 100-1,000 people and generate substantial revenue while maintaining some entrepreneurial characteristics.
Medium business features:
- Professional management structures
- Multiple product lines or service offerings
- Regional or national market presence
- Access to commercial lending and investment
- Established operational systems
Large Enterprises
Large enterprises employ thousands of people and generate billions in annual revenue. These organizations often operate internationally and significantly impact their industries and economies.
Enterprise characteristics:
- Complex organizational structures
- Global market presence
- Substantial capital resources
- Sophisticated technology systems
- Significant regulatory compliance requirements
Apple exemplifies a successful large enterprise that began as a small startup in 1976. Through continuous innovation, strategic partnerships, and excellent execution, Apple transformed from a garage-based operation into one of the world’s most valuable companies. Their success demonstrates how businesses can evolve from small beginnings to global dominance.
For businesses looking to expand, understanding digital transformation strategies becomes crucial for competing in modern markets.
Business Models and Operations
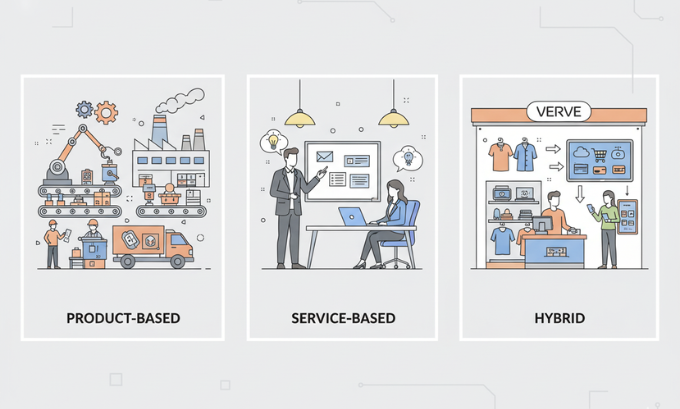
Product-Based Businesses
Product-based businesses create, manufacture, or distribute physical goods to customers. These enterprises require supply chain management, inventory control, and distribution networks.
Examples include:
- Manufacturing companies producing automobiles, electronics, or clothing
- Retail businesses selling consumer goods
- Food production and distribution companies
Tesla represents an innovative product-based business that revolutionized the automotive industry. By focusing on electric vehicles and sustainable energy solutions, Tesla created new market categories while challenging established automotive manufacturers. Their pre-sales strategy and direct-to-consumer model demonstrate how product businesses can innovate beyond traditional approaches.
Service-Based Businesses
Service businesses provide intangible offerings such as expertise, labor, or specialized knowledge. These enterprises typically require less capital investment than product businesses but depend heavily on human resources and customer relationships.
Service business categories:
- Professional services (consulting, legal, accounting)
- Personal services (healthcare, education, entertainment)
- Business services (marketing, IT support, logistics)
Hybrid Business Models
Many modern businesses combine product and service elements to create comprehensive customer solutions. This approach often provides more stable revenue streams and stronger customer relationships.
Nike started as a product company focused on athletic footwear but evolved into a lifestyle brand offering products, services, and experiences. Their transformation from a narrow athletic shoe company to a global lifestyle brand demonstrates successful business model evolution.
To understand more about business development strategies, explore resources on how to start a business that cover various operational models and approaches.
Essential Business Terminology
Business Administration
What is a business administration degree? Business administration education provides comprehensive training in management principles, financial analysis, marketing strategies, and operational efficiency. This degree prepares individuals for leadership roles across various industries and business functions.
Business administration encompasses:
- Strategic planning and decision-making
- Financial management and budgeting
- Human resources and organizational behavior
- Marketing and sales management
- Operations and supply chain management
Business Plans and Documentation
What is a business plan? A business plan serves as a comprehensive document outlining business objectives, strategies, financial projections, and operational approaches. This essential tool helps entrepreneurs secure funding, guide operations, and measure progress.
Key business plan components:
- Executive summary and company description
- Market analysis and competitive landscape
- Marketing and sales strategies
- Management and organizational structure
- Financial projections and funding requirements
What is a business proposal? Business proposals present specific solutions, services, or partnerships to potential clients or partners. Unlike business plans (internal planning documents), proposals target external audiences and focus on meeting specific needs or opportunities.
Financial and Legal Concepts
What is a business line of credit? A business line of credit provides flexible access to funds up to a predetermined limit. Unlike traditional loans, businesses only pay interest on amounts actually used, making this financing option ideal for managing cash flow and unexpected expenses.
What is a business entity? A business entity represents the legal structure chosen for conducting business activities. The entity type affects taxation, liability, ownership transfer, and regulatory compliance requirements.
What is a business trust? Business trusts involve holding business assets or interests for the benefit of designated beneficiaries. This structure can provide tax advantages, estate planning benefits, and operational flexibility in certain situations.
For entrepreneurs seeking practical guidance, comprehensive resources on low-cost marketing ideas for startups offer valuable strategies for building successful enterprises.
Business Operations and Management
Business Analysis and Strategy
What is a business analyst? Business analysts serve as bridges between business needs and technical solutions. They analyze organizational processes, identify improvement opportunities, and recommend strategies for enhanced efficiency and effectiveness.
Business analyst responsibilities:
- Requirements gathering and documentation
- Process mapping and analysis
- Stakeholder communication and coordination
- Solution design and implementation support
- Performance measurement and optimization
Business Consulting Services
What is a business consultant? Business consultants provide expert advice and specialized knowledge to help organizations solve problems, improve performance, and achieve strategic objectives. They bring external perspectives and proven methodologies to address complex business challenges.
Consulting service areas:
- Strategy development and implementation
- Operational efficiency improvements
- Technology integration and digital transformation
- Financial analysis and restructuring
- Change management and organizational development
Business Continuity Planning
What is a business continuity plan? Business continuity plans outline procedures for maintaining operations during disruptions such as natural disasters, cyber attacks, or economic downturns. These plans help minimize losses and ensure rapid recovery.
Continuity planning elements:
- Risk assessment and impact analysis
- Emergency response procedures
- Communication protocols
- Alternative operating arrangements
- Recovery strategies and timelines
Walmart demonstrates excellent business continuity planning through their robust supply chain management and disaster response capabilities. During natural disasters or supply disruptions, Walmart’s systems enable continued operations and community support, showcasing how large enterprises can maintain resilience.
Business Cycles and Market Dynamics
Understanding Business Cycles
What is a business cycle? Business cycles represent recurring patterns of economic expansion and contraction that affect business performance across industries and regions. Understanding these cycles helps businesses plan for varying market conditions.
Business cycle phases:
- Expansion: Growing economic activity, increasing demand, rising employment
- Peak: Maximum economic activity before decline begins
- Contraction: Declining economic activity, reduced demand, increasing unemployment
- Trough: Minimum economic activity before recovery begins
Business Opportunities and Market Analysis
What is a business opportunity? Business opportunities represent favorable circumstances for starting new ventures, expanding existing operations, or entering new markets. Successful entrepreneurs identify and capitalize on these opportunities through careful analysis and strategic action.
Opportunity identification factors:
- Market gaps and unmet customer needs
- Technological advances and innovations
- Regulatory changes and policy shifts
- Demographic trends and social changes
- Economic conditions and industry dynamics
Go Ape provides an excellent example of identifying unique business opportunities. By recognizing the growing demand for outdoor adventure experiences and utilizing existing forest resources through partnerships, they created a successful business model without massive capital investment in land acquisition.
For entrepreneurs exploring various opportunities, resources on e-commerce business ideas for beginners offer insights into growing digital markets.
Starting and Growing a Business
Initial Business Development
Starting a business requires careful planning, resource allocation, and strategic decision-making. Successful entrepreneurs follow systematic approaches that increase their chances of long-term success.
Essential startup steps:
- Market research and opportunity validation
- Business model development and testing
- Legal structure selection and registration
- Financial planning and funding acquisition
- Team building and operational setup
The business registration number obtained during the legal formation process serves as an official identifier enabling legitimate business operations, tax compliance, and access to business services.
Entrepreneurship Mindsets and Approaches
Entrepreneurship encompasses various approaches to creating and growing businesses. Successful entrepreneurs often share common characteristics while adapting their strategies to specific market conditions and opportunities.
Entrepreneurial approaches:
- Innovation-driven: Focus on creating new products, services, or business models
- Market-driven: Identify and serve underserved market segments
- Technology-enabled: Leverage technological advances for competitive advantage
- Social entrepreneurship: Address social problems while generating sustainable returns
Uber represents disruptive entrepreneurship that challenged traditional regulatory frameworks and established business models. By leveraging mobile technology and creating new service categories, Uber demonstrated how entrepreneurial ventures can transform entire industries despite regulatory resistance.
Business Growth and Scaling Strategies
Growing businesses face unique challenges requiring different approaches than startup phases. Understanding how to scale a business successfully involves developing systems, processes, and capabilities that support expanded operations.
Growth strategies:
- Market expansion into new geographic regions
- Product line extensions and diversification
- Strategic partnerships and acquisitions
- Technology adoption and automation
- Team development and organizational structure optimization
For businesses exploring international expansion, specialized resources on becoming an Amazon seller in Japan provide valuable insights into specific market opportunities.
Professional Development and Business Education
Business Administration Career Paths
Business administration education opens doors to diverse career opportunities across industries and functional areas. Graduates can pursue roles in management, consulting, entrepreneurship, or specialized business functions.
Career opportunities:
- General management and executive leadership
- Financial analysis and corporate finance
- Marketing and brand management
- Operations and supply chain management
- Strategic planning and business development
Continuous Learning and Skill Development
The evolving business landscape requires continuous learning and adaptation. Professionals benefit from staying current with industry trends, emerging technologies, and management best practices.
Professional development areas:
- Digital literacy and technology integration
- Data analysis and decision-making skills
- Leadership and communication abilities
- Industry-specific knowledge and expertise
- Global business understanding and cultural competency
For those interested in expanding their knowledge about Amazon FBA and e-commerce strategies, specialized resources provide detailed guidance on modern business opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a business day and a calendar day?
What is a business day? A business day typically refers to Monday through Friday, excluding holidays, when normal business operations occur. This distinction is important for contracts, payment terms, and service delivery schedules. Most financial transactions, legal proceedings, and business communications operate on business day schedules.
How do I choose the right business structure?
The appropriate business structure depends on factors including liability protection needs, tax considerations, ownership structure, and growth plans. Sole proprietorships suit simple operations, while LLCs offer flexibility and protection. Corporations provide maximum liability protection but involve more complexity. Consulting with legal and tax professionals helps determine the optimal choice.
What makes a business plan effective?
Effective business plans clearly articulate the value proposition, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. They should be realistic, well-researched, and regularly updated. The best business plans demonstrate deep market understanding and present compelling cases for success while acknowledging potential risks and mitigation strategies.

How much capital do I need to start a business?
Capital requirements vary dramatically by industry, business model, and scale. Service businesses often require less initial investment than product-based enterprises. Consider all startup costs including equipment, inventory, marketing, legal fees, and operating expenses for the first 6-12 months. Many successful businesses start small and reinvest profits for growth.
What is the role of business registration?
Business registration provides legal recognition, enables tax compliance, and allows access to business services and protections. The registration process varies by location and business type but typically involves selecting a business name, choosing a structure, filing appropriate documents, and obtaining necessary licenses or permits.
How can I identify good business opportunities?
Successful business opportunities often address unmet market needs, leverage emerging technologies, or improve existing solutions. Stay alert to market trends, customer complaints, regulatory changes, and technological advances. Network with other entrepreneurs, conduct market research, and validate ideas through customer feedback before making significant investments.
What is the importance of business continuity planning?
Business continuity planning helps organizations prepare for and respond to disruptions that could threaten operations. These plans identify critical business functions, establish alternative operating procedures, and outline recovery strategies. Proper continuity planning reduces downtime, protects revenue, and maintains customer confidence during challenging periods.
Building Your Business Foundation for Long-term Success
Understanding what constitutes a business extends far beyond simple profit-making activities. Modern businesses operate as complex organizations that create value, serve communities, and drive economic progress. Whether you’re considering entrepreneurship or seeking to understand business concepts, recognizing the various structures, sizes, and operational models provides essential knowledge for success.
The journey from business concept to successful enterprise requires careful planning, strategic decision-making, and continuous adaptation. Successful companies like Apple, Tesla, and Walmart demonstrate how businesses can evolve from small beginnings into global leaders through innovation, excellent execution, and customer focus.
The business landscape continues evolving with technological advances, changing consumer preferences, and global economic shifts. Entrepreneurs and business professionals who stay informed about emerging trends, develop relevant skills, and maintain adaptability position themselves for success in dynamic markets.
Whether you’re starting your first business, scaling an existing operation, or pursuing business education, the fundamental principles outlined in this guide provide a solid foundation for understanding and navigating the complex world of business. Success requires combining this knowledge with practical experience, continuous learning, and strategic action in pursuit of your business objectives.
For additional insights into business development and entrepreneurship strategies, explore the comprehensive resources available through the referenced platforms and continue building your business knowledge base.
Meta data
Meta title:
What Is a Business? Complete Guide to Types & Company Sizes
Meta description:
Discover what defines a business, explore different types of business structures, company sizes, and essential terminology for entrepreneurs and business professionals.
Author Bio:
This comprehensive business guide was created by experienced business professionals with extensive knowledge in entrepreneurship, corporate strategy, and business development. Our team has helped hundreds of businesses navigate complex challenges and achieve sustainable growth through proven strategies and practical insights.
References:
- Small Business Administration (SBA) – Official guidelines and business resources
- U.S. Department of Commerce – Business statistics and industry data
- Harvard Business Review – Strategic management and business analysis
- McKinsey & Company – Business transformation and growth strategies
- Investopedia – Financial and business terminology definitions

